Mass Spectrometry Databases and Data Format of Spectral Multifiles: Difference between pages
mNo edit summary |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Spectral multifiles combine multiple spectra in one single file. These files are stored in a Matlab™ specific data format and contain the spectral as well as the respective metadata. Spectral multifiles can be loaded in Matlab by entering the following command: | |||
>> load('ecoli-filelist-oct16.muf','-mat') | |||
This command will open ''ecoli-filelist-oct16.muf'', an example multifile containing 16 individual MALDI-TOF mass spectra acquired from five different strains of ''E. coli''. The file ''ecoli-filelist-oct16.muf'' can be downloaded [http://wiki.microbe-ms.com/upload/ecoli-filelist-oct16.muf: '''here''']. If loading was successful, you will have access to a new Matlab variable ''spec'' (structure array). Details of the structure of ''spec'' are described next.<br> <br> | |||
'''Fields of the structure array ''spec''''': | |||
{| class="wikitable" width=1100 | |||
!width=100| Fields | |||
!width=600| Description | |||
!width=100| Data type | |||
!width=300| | |||
|- | |||
| org | |||
| original mass spectra [2 x n array], n: number of data points | |||
| float32 | |||
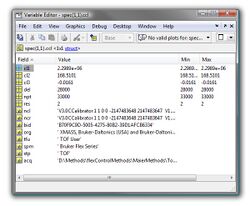
| rowspan="35" style="background: #ffffff;" valign="top" | [[File:Multifile-format-spec-struc.jpg|250px|thumb|center|Matlab screenshot - format of a spectral multifile (*.muf) demonstrating the general structure of the structure array 'spec'. In this example the metadata of spectrum #17 are shown. Spectrum #17 is a data base spectrum which has been created from 8 individual mass spectra (cf. spec(1,17).dbs)]] | |||
|- | |||
| pre | |||
| pre-processed spectra [2 x n array], n: number of data points | |||
| float32 | |||
|- | |||
| nam | |||
| spectra id | |||
| string | |||
|- | |||
| gen | |||
| genus information | |||
| string | |||
|- | |||
| spe | |||
| species info | |||
| string | |||
|- | |||
| str | |||
| strain info | |||
| string | |||
|- | |||
| typ | |||
| type | |||
| string | |||
|- | |||
| uid | |||
| taxonomy identification number for species as used by the NCBI (see [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi]) | |||
| integer | |||
|- | |||
| uie | |||
| taxonomy identification number for strains used by the NCBI (see [https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Taxonomy/Browser/wwwtax.cgi]) | |||
| interger | |||
|- | |||
| gti | |||
| cultivation conditions: growth time | |||
| string | |||
|- | |||
| tem | |||
| cultivation conditions: cultivation temperature | |||
| string | |||
|- | |||
| air | |||
| cultivation conditions: cultivation under aerobic or anaerobic conditions | |||
| string | |||
|- | |||
| med | |||
| cultivation conditions: cultivation medium | |||
| string | |||
|- | |||
| spo | |||
| spore formers (YES or NO) | |||
| string | |||
|- | |||
| con | |||
| sample concentration | |||
| string | |||
|- | |||
| trt | |||
| sample treatment | |||
| string | |||
|- | |||
| ext | |||
| extra information | |||
| string | |||
|- | |||
| las | |||
| laser parameters (power, diameter, frequency, etc.) | |||
| string | |||
|- | |||
| cal | |||
| calibration info | |||
| string | |||
|- | |||
| met | |||
| measurement method | |||
| string | |||
|- | |||
| cus | |||
| customer info | |||
| string | |||
|- | |||
| tim | |||
| date and time of measurement | |||
| string | |||
|- | |||
| pth | |||
| path to spectrum | |||
| string | |||
|- | |||
| pik | |||
| [[#peak table format|peak table]], an array of the dimension [4 x npeaks] npeaks: number of peaks | |||
| float32 | |||
|- | |||
| cls | |||
| class assignment (valid values are 0,1,2,3 and 4) | |||
| float32 | |||
|- | |||
| lms | |||
| MALDI-TOF or LC-MS spectrum? (valid values are 0 [MALDI] and 1 [LC-MS]) | |||
| float32 | |||
|- | |||
| lst | |||
| formatted text containing the peak table | |||
| char array | |||
|- | |||
| seq | |||
| sequence of pre-processing steps | |||
| string | |||
|- | |||
| smo | |||
| the number of smoothing points (Savitzky-Golay smoothing) | |||
| float32 | |||
|- | |||
| bas | |||
| number of intervals used for baseline correction | |||
| float32 | |||
|- | |||
| nrm | |||
| normalization parameter (Yes:1, No:0) | |||
| float32 | |||
|- | |||
| clb | |||
| calibration paarmeters (see below for details) | |||
| float32 | |||
|- | |||
| red | |||
| data reduction factor (spectral binning) | |||
| string | |||
|- | |||
| cut | |||
| cut in the spectral domain | |||
| string | |||
|- | |||
| mod | |||
| original data modified by cut or red (Yes:1, No:0) | |||
| float32 | |||
|- | |||
| prm | |||
| parameters of peak detection | |||
| string | |||
|- | |||
| ccl | |||
| [[#structure array ccl|calibration information]] (see below) | |||
| structure array | |||
|- | |||
| dbs | |||
| [[#structure array dbs|data base spectrum]] (Yes:1, No:0) | |||
| structure array | |||
|- | |||
| avr | |||
| [[#structure array avr|average spectrum]] (Yes:1, No:0) | |||
| structure array | |||
|} | |||
<span class="mw-headline" id="peak table format">'''Format of peak tables''' (spec.pik):</span> | |||
== | {| class="wikitable" width=800 | ||
!width=100| Fields | |||
!width=700| Description | |||
|- | |||
| spec.pik(1,:) <br> <br> | |||
| m/z positions of the peaks in the peak table <br> <br> | |||
|- | |||
| spec.pik(2,:) <br> <br> | |||
| absolute intensities of these peaks <br> <br> | |||
|- | |||
| spec.pik(3,:) <br> <br> | |||
| weighting factors (the sum of these factors equals 100) <br> <br> | |||
|- | |||
| spec.pik(4,:) <br> <br> | |||
| in case of single spectra, i.e. no database or average spectra: baseline-corrected absolute intensities of the peaks, in case of average or database spectra: the relative peak frequency | |||
|} | |||
<span class="mw-headline" id="structure array ccl">'''Calibration Information''' (spec.ccl):</span> | |||
{| class="wikitable" width=1100 | |||
!width=100| Fields | |||
!width=600| Description | |||
!width=100| Type | |||
!width=300| | |||
|- | |||
| cl1 | |||
| calibration constant 1 | |||
| float32 | |||
| rowspan="15" style="background: #ffffff;" valign="top" | [[File:Array-spec-ccl.jpg|250px|thumb|center|Matlab screenshot - format of structure array spec.ccl containing the calibration info, such as calibration constants, delay time, number of spectra data points, etc. for spectrum #1.]] | |||
|- | |||
| cl2 | |||
| calibration constant 2 | |||
| float32 | |||
|- | |||
| cl3 | |||
| calibration constant 3 | |||
| float32 | |||
|- | |||
| del | |||
| delay time [ns] | |||
| float32 | |||
|- | |||
| npt | |||
| number of data points | |||
| float32 | |||
|- | |||
| res | |||
| time resolution [ns] | |||
| float32 | |||
|- | |||
| ncl | |||
| calibration info required to store the spectrum in a Bruker-specific data format | |||
| string | |||
|- | |||
| ncr | |||
| calibration info required to store the spectrum in a Bruker-specific data format | |||
| string | |||
|- | |||
| bid | |||
| hardware id of the spectrum | |||
| string | |||
|- | |||
| org | |||
| manufacturer info | |||
| string | |||
|- | |||
| tfu | |||
| manufacturer info | |||
| string | |||
|- | |||
| tfu | |||
| software info, required for compatibility issues | |||
| string | |||
|- | |||
| spm | |||
| type of instrumentation | |||
| string | |||
|- | |||
| stp | |||
| type of measurement (should be 'TOF') | |||
| string | |||
|- | |||
| acq | |||
| path to the original spectrum | |||
| string | |||
|} | |||
<span class="mw-headline" id="structure array dbs">'''Data Base Spectrum''' (spec.dbs):</span> | |||
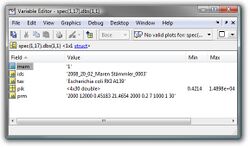
A [[Create database spectra|database spectrum]] is usually created from many (>3) individual mass spectra. The structure array ''spec.dbs'' contains information (metadata, peak tables) on the mass spectra used to produce the given database spectrum. Details of the structure of ''spec.dbs'' are given in the table below. | |||
{| class="wikitable" width=1100 | |||
!width=100| Fields | |||
!width=600| Description | |||
!width=100| Type | |||
!width=300| | |||
|- | |||
| mem | |||
| string defining if the current spectrum is a data base spectrum (1) or not (0) | |||
| string | |||
| rowspan="5" style="background: #ffffff;" valign="top" |[[File:Array-spec-dbs.jpg|250px|thumb|center|Matlab screenshot - format of structure array spec.dbs. spec(1,17).dbs(1,1) contains information of mass spectrum #1 which was used with others to obtain data base spectrum #17, such as the id, taxonomic information, peak tables and the respective peak detection parameters).]] | |||
|- | |||
| ids | |||
| id of the individual mass spectrum used to create the data base spectrum | |||
| string | |||
|- | |||
| tax | |||
| taxonomic info of the source spectrum | |||
| string | |||
|- | |||
| pik | |||
| peak table of the source spectrum | |||
| float32 | |||
|- | |||
| prm | |||
| parameters of peak detection | |||
| string | |||
|} | |||
<span class="mw-headline" id="structure array avr">'''Average Spectrum''' (spec.avr):</span> | |||
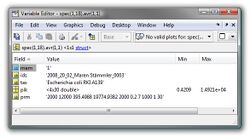
An [[Averaging Mass Spectra|average spectrum]] is usually created from many (>3) individual mass spectra. The structure array ''spec.avr'' contains information (metadata, peak tables) on the mass spectra used to produce the given avarage spectrum. Details of the structure of ''spec.avr'' are given in the table below. | |||
{| class="wikitable" width=1100 | |||
!width=100| Fields | |||
!width=600| Description | |||
!width=100| Type | |||
!width=300| | |||
|- | |||
| mem | |||
| string defining if the current spectrum is a data base spectrum (1) or not (0) | |||
| string | |||
| rowspan="5" style="background: #ffffff;" valign="top" |[[File:Array-spec-avr.jpg|250px|thumb|center|Matlab screenshot - format of structure array spec.avr. spec(1,18).avr(1,1) contains information of mass spectrum #1 which was used with others to obtain an average spectrum #18, such as the id, taxonomic information, peak tables and the respective peak detection parameters).]] | |||
|- | |||
| ids | |||
| id of the individual mass spectrum used to create the avarage spectrum | |||
| string | |||
|- | |||
| tax | |||
| taxonomic info of the source spectrum | |||
| string | |||
|- | |||
| pik | |||
| peak table of the source spectrum | |||
| float32 | |||
|- | |||
| prm | |||
| parameters of peak detection | |||
| string | |||
|} | |||
Latest revision as of 17:32, 21 March 2023
Spectral multifiles combine multiple spectra in one single file. These files are stored in a Matlab™ specific data format and contain the spectral as well as the respective metadata. Spectral multifiles can be loaded in Matlab by entering the following command:
>> load('ecoli-filelist-oct16.muf','-mat')
This command will open ecoli-filelist-oct16.muf, an example multifile containing 16 individual MALDI-TOF mass spectra acquired from five different strains of E. coli. The file ecoli-filelist-oct16.muf can be downloaded here. If loading was successful, you will have access to a new Matlab variable spec (structure array). Details of the structure of spec are described next.
Fields of the structure array spec:
| Fields | Description | Data type | |
|---|---|---|---|
| org | original mass spectra [2 x n array], n: number of data points | float32 | |
| pre | pre-processed spectra [2 x n array], n: number of data points | float32 | |
| nam | spectra id | string | |
| gen | genus information | string | |
| spe | species info | string | |
| str | strain info | string | |
| typ | type | string | |
| uid | taxonomy identification number for species as used by the NCBI (see [1]) | integer | |
| uie | taxonomy identification number for strains used by the NCBI (see [2]) | interger | |
| gti | cultivation conditions: growth time | string | |
| tem | cultivation conditions: cultivation temperature | string | |
| air | cultivation conditions: cultivation under aerobic or anaerobic conditions | string | |
| med | cultivation conditions: cultivation medium | string | |
| spo | spore formers (YES or NO) | string | |
| con | sample concentration | string | |
| trt | sample treatment | string | |
| ext | extra information | string | |
| las | laser parameters (power, diameter, frequency, etc.) | string | |
| cal | calibration info | string | |
| met | measurement method | string | |
| cus | customer info | string | |
| tim | date and time of measurement | string | |
| pth | path to spectrum | string | |
| pik | peak table, an array of the dimension [4 x npeaks] npeaks: number of peaks | float32 | |
| cls | class assignment (valid values are 0,1,2,3 and 4) | float32 | |
| lms | MALDI-TOF or LC-MS spectrum? (valid values are 0 [MALDI] and 1 [LC-MS]) | float32 | |
| lst | formatted text containing the peak table | char array | |
| seq | sequence of pre-processing steps | string | |
| smo | the number of smoothing points (Savitzky-Golay smoothing) | float32 | |
| bas | number of intervals used for baseline correction | float32 | |
| nrm | normalization parameter (Yes:1, No:0) | float32 | |
| clb | calibration paarmeters (see below for details) | float32 | |
| red | data reduction factor (spectral binning) | string | |
| cut | cut in the spectral domain | string | |
| mod | original data modified by cut or red (Yes:1, No:0) | float32 | |
| prm | parameters of peak detection | string | |
| ccl | calibration information (see below) | structure array | |
| dbs | data base spectrum (Yes:1, No:0) | structure array | |
| avr | average spectrum (Yes:1, No:0) | structure array |
Format of peak tables (spec.pik):
| Fields | Description |
|---|---|
| spec.pik(1,:) |
m/z positions of the peaks in the peak table |
| spec.pik(2,:) |
absolute intensities of these peaks |
| spec.pik(3,:) |
weighting factors (the sum of these factors equals 100) |
| spec.pik(4,:) |
in case of single spectra, i.e. no database or average spectra: baseline-corrected absolute intensities of the peaks, in case of average or database spectra: the relative peak frequency |
Calibration Information (spec.ccl):
| Fields | Description | Type | |
|---|---|---|---|
| cl1 | calibration constant 1 | float32 | |
| cl2 | calibration constant 2 | float32 | |
| cl3 | calibration constant 3 | float32 | |
| del | delay time [ns] | float32 | |
| npt | number of data points | float32 | |
| res | time resolution [ns] | float32 | |
| ncl | calibration info required to store the spectrum in a Bruker-specific data format | string | |
| ncr | calibration info required to store the spectrum in a Bruker-specific data format | string | |
| bid | hardware id of the spectrum | string | |
| org | manufacturer info | string | |
| tfu | manufacturer info | string | |
| tfu | software info, required for compatibility issues | string | |
| spm | type of instrumentation | string | |
| stp | type of measurement (should be 'TOF') | string | |
| acq | path to the original spectrum | string |
Data Base Spectrum (spec.dbs):
A database spectrum is usually created from many (>3) individual mass spectra. The structure array spec.dbs contains information (metadata, peak tables) on the mass spectra used to produce the given database spectrum. Details of the structure of spec.dbs are given in the table below.
| Fields | Description | Type | |
|---|---|---|---|
| mem | string defining if the current spectrum is a data base spectrum (1) or not (0) | string | |
| ids | id of the individual mass spectrum used to create the data base spectrum | string | |
| tax | taxonomic info of the source spectrum | string | |
| pik | peak table of the source spectrum | float32 | |
| prm | parameters of peak detection | string |
Average Spectrum (spec.avr):
An average spectrum is usually created from many (>3) individual mass spectra. The structure array spec.avr contains information (metadata, peak tables) on the mass spectra used to produce the given avarage spectrum. Details of the structure of spec.avr are given in the table below.
| Fields | Description | Type | |
|---|---|---|---|
| mem | string defining if the current spectrum is a data base spectrum (1) or not (0) | string | |
| ids | id of the individual mass spectrum used to create the avarage spectrum | string | |
| tax | taxonomic info of the source spectrum | string | |
| pik | peak table of the source spectrum | float32 | |
| prm | parameters of peak detection | string |