Peak Detection: Difference between revisions
| (50 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
Peak picking is an essential (and the final) step of the spectral pre-processing pipeline. The result of peak picking is a peak table which is attached to the mass spectra. In MicrobeMS peak picking can be started via the ''find peaks'' command of the ''Peak pick'' pulldown menu (shortcut <ctrl>+P), or by pressing the ''peak'' button located in the ''Peak pick'' tab. | Peak picking is an essential (and the final) step of the spectral pre-processing pipeline. The result of peak picking is a peak table which is attached to the mass spectra. In MicrobeMS peak picking can be started via the ''find peaks'' command of the ''Peak pick'' pulldown menu (shortcut <ctrl>+P), or by pressing the ''peak'' button located in the ''Peak pick'' tab. | ||
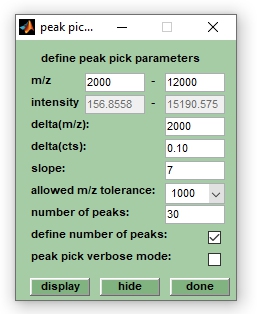
[[File:Peak-pick.jpg|right|Screenshot of the peak pick | [[File:Peak-pick.jpg|right|Screenshot of the peak pick user dialog box]] | ||
== Peak picking - basic concepts == | == Peak picking - basic concepts == | ||
Peak picking in MicrobeMS is always carried out on the basis of original, or pre-processed mass spectra, i.e. the content of existing peak table produced by software packages from other vendors will be ignored. The key idea of peak picking in MicrobeMS is based on two observations. Firstly, it is often convenient to limit the number of peaks per mass spectrum to pre-defined values. Secondly, the analytical sensitivity of MALDI- | Peak picking in MicrobeMS is always carried out on the basis of original, or pre-processed mass spectra, i.e. the content of existing peak table produced by software packages from other vendors will be ignored. The key idea of peak picking in MicrobeMS is based on two observations. Firstly, it is often convenient to limit the number of peaks per mass spectrum to pre-defined values. Secondly, the analytical sensitivity of MALDI-ToF mass spectrometry is different in different m/z regions: The sensitivity is higher in the low m/z region and lower in the high m/z region. | ||
These two observations are addressed with the procedure described next: | These two observations are addressed with the procedure described next: | ||
The first step of peak detection in MicrobeMS involves the generation of a ''so called'' threshold function represented by a S-shaped curve. Peaks can only be identified at m/z values with intensities above the threshold. In MicrobeMS the threshold function for peak picking is defined as the sum of the following m/z dependencies: | The first step of peak detection in MicrobeMS involves the generation of a ''so called'' threshold function represented by a S-shaped curve. Peaks can only be identified at m/z values with intensities above the threshold. In MicrobeMS the threshold function for peak picking is defined as the sum of the following m/z dependencies: | ||
i) A baseline function obtained by baseline correction by asymmetric least squares, | :i) A baseline function obtained by [https://wiki-ms.microbe-ms.com/index.php?title=Spectral_Pre-processing#Baseline_subtraction baseline correction by asymmetric least squares], | ||
ii) | :ii) a S-shaped sigmoid function <math>T_{m/z}</math> that reflects MALDI-ToF MS sensitivity as a function of m/z values, and | ||
iii) | :iii) the noise distribution function multiplied by a constant. | ||
[[File:Threshold-for-peak-picking.jpg| | [[File:Threshold-for-peak-picking.jpg|600px|thumb|right| Sigmoidal function <math>T_{m/z}</math> used for peak picking. Note that the parameters indicated are used for illustration purposes and are generally not recommended for peak picking. The slope parameter ''l'' which equals 5.5 in this example (default is 7.5) defines the the slope of the curve at the x-position <math>x_{c}</math>. The latter parameter defines the point at which asymptote maximum (pos, or neg) growth occurs (in this example at <math>x_{c}</math> = 8000 Th).]] | ||
The | The sigmoid function <math>T_{m/z}</math> (ii) is a special type of a [https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Generalised_logistic_function generalized logistic function], which is defined by the following equation: | ||
::<math>T_{m/z} = {I_{m,s} \over (1+e^{k*(x-x_{c})})}</math> (1), | |||
:<math> | where | ||
::<math>k = e^{-l}</math> (2) and <math>I_{m,s} = I_{m}*s</math> (3) | |||
:<math> | {| | ||
|- style="vertical-align:top;" | |||
|<math>T_{m/z}</math> | |||
|the intensity threshold function, i.e. the S-shaped sigmoid function | |||
|- style="vertical-align:top;" | |||
|<math>I_{m}</math> | |||
|mean of the 13(-3) most intense mass peaks in the m/z range [mzlow mzhigh] of the given mass spectrum, 13(-3) means that the top 3 mass peaks are ignored | |||
|- style="vertical-align:top;" | |||
|<math>s</math> | |||
|variable scaling factor of <math>I_{m}</math> | |||
|- style="vertical-align:top;" | |||
|<math>l</math> | |||
|slope, affects the slope of the threshold function around <math>x_{c}</math> | |||
|- style="vertical-align:top;" | |||
|<math>x_{c}</math> | |||
|'center' of the sigmoidal function, denotes the x-position at which asymptote maximum growth (pos, or neg) occurs | |||
|- style="vertical-align:top;" | |||
|<math>x</math> | |||
|the x-vector (in Th units) ranging from mzlow to mzhigh (2000 - 13000 Th per default) | |||
|} | |||
To obtain the peak tables the intensity threshold function T(m/z) is automatically obtained on the basis of parameters indicated in the window ''peak pick parameters''. If the checkbox ''define number of peaks'' is not checked peak tables will contain only peaks with intensities larger than the threshold function. Otherwise the threshold function is scaled iteratively until the desired number of peaks is obtained. | |||
When peak picking | When peak picking is complete a peak table array is created with ''npeaks'' rows and ''four'' or ''six'' columns (''npeaks'' is the number of peaks in the table, see below for a description of the contents of the peak table). Peak tables are automatically added to the corresponding MS spectra and are displayed in a list box on the left side of the MicrobeMS main window, below the list box with the ''MicrobeMS spectra IDs''. Note that existing peak tables may be overwritten without warning when new peak tables are created. Some computational details of the peak picking routine are available from the command line window if the ''peak pick verbose mode'' check box has been selected. | ||
== Peak picking - the procedure == | == Peak picking - the procedure == | ||
| Line 52: | Line 56: | ||
To produce peak tables from raw mass spectra the following sequence of steps needs to be taken: | To produce peak tables from raw mass spectra the following sequence of steps needs to be taken: | ||
1. Load the mass spectral data files via the [[Load spectra (Bruker format)|load spectra]] (Bruker data file format), [[Import Mass Spectra in a mzXML Data Format|import spectra from mzXML data]], or the ''load MS multifile'' options of the ''File'' pull down menu. | |||
2. Perform [[Spectral Pre-processing|spectral pre-processing]] | |||
3. Select the respective mass spectra in the list box at the top left corner (the list box is labeled by ''MicrobeMS spectra ID`s''). To select multiple spectra hold the <shift> key while selecting. | |||
4. Choose ''Peak pick parms'' (shortcut: <ctrl>+M) from the ''Peak pick'' pull down menu, or alternatively, press the button ''more'' in the ''Pick pick'' panel located at the central bottom of the main figure of MicrobeMS. A window entitled ''peak pick parameters'' comes up. Modify parameters of peak pick if necessary. When pressing the button ''display'' the intensity threshold function will be displayed. ''Hide'' removes this function from display. Press ''done'' to close this window, the values of modified parameters are not lost by this operation. | |||
5. To start peak picking press the button ''peak'' (''Peak pick'' panel) or select ''find peaks''(shortcut: <ctrl>+P) from the ''Peak pick'' pull down menu. In cases where more than one spectrum has been selected a progress indicator will inform on the status of peak picking. | |||
== Format of | == Format of peak tables == | ||
When peak picking has been finished, a peak table array containing ''npeaks'' rows and ''four'' columns is created (npeaks denotes the number of peaks in the table). The peak tables are attached to the spectral data files and contain the following columns: | When peak picking has been finished, a peak table array containing ''npeaks'' rows and ''four'' columns is created (npeaks denotes the number of peaks in the table). The peak tables are attached to the spectral data files and contain the following columns: | ||
| Line 77: | Line 72: | ||
* column #1: the m/z positions of the peaks | * column #1: the m/z positions of the peaks | ||
* column #2: the respective intensity values (intensity units). Note that the intensity values may represent intensities after baseline correction and normalization in cases where peak tables were obtained from pre-processed spectra. | * column #2: the respective intensity values (intensity units). Note that the intensity values may represent intensities after baseline correction and normalization in cases where peak tables were obtained from pre-processed spectra. | ||
* column #3: weighting factors (''weights''): these factors are obtained by scaling the values of column #2 (in a 1-norm manner) such that the sum of weighting factors contained in a given peak list equals | * column #3: weighting factors (''weights''): these factors are obtained by scaling the values of column #2 (in a 1-norm manner) such that the sum of weighting factors contained in a given peak list equals 1000. Note that the ratios between the peak intensities are preserved. | ||
* column #4: contains the intensity values of the threshold function (see above) at the m/z positions given by column #1 | * column #4: contains the intensity values of the threshold function (see above) at the m/z positions given by column #1 | ||
* column #5: FWHM (full width at half maximum) of the given peak (not always present, requires QT) | |||
* column #6: resolving power of the peak (not always present, requires QT) | |||
See also [[Data_Format_of_Peak_List_Files|Description of the format of peak list files (*.pkf)]] | See also [[Data_Format_of_Peak_List_Files|Description of the format of peak list files (*.pkf)]] | ||
== Function ''view peak | == Function ''view peak tables'' == | ||
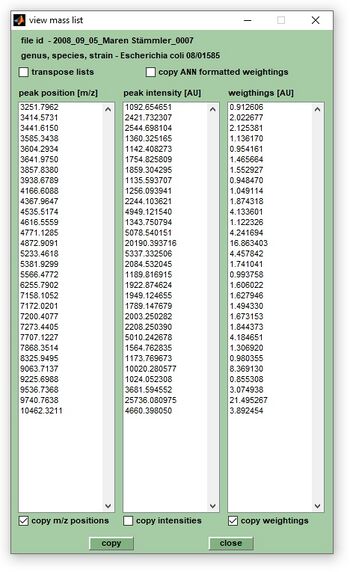
This function allows to view and copy peak list data. Press the ''view'' button in the ''Peak pick'' panel tab to view peak list data (see screenshot below). | This function allows to view and copy peak list data. Press the ''view'' button in the ''Peak pick'' panel tab to view peak list data (see screenshot below). | ||
| Line 89: | Line 86: | ||
|- style="vertical-align:top;" | |- style="vertical-align:top;" | ||
|[[File:View-peak-list.jpg|350px|thumb|right|View & copy peak list data]] | |[[File:View-peak-list.jpg|350px|thumb|right|View & copy peak list data]] | ||
| style="width:400px;" | <br>To copy the content of the columns '' | | style="width:400px;" | <br>To copy the content of the columns ''peak positions [m/z]'', ''peak intensity [AU]'' (peak intensities from original, or pre-processed spectra), ''weightings [AU]'' (peak weighting factors), ''FWHM values'' (in m/z units), and, or ''resolving power'', check the appropriate check boxes at the bottom of the dialog box and press ''copy''. | ||
Checkbox ''transpose lists'': Columns are rotated by 90 degrees if checked (i.e. columns are transposed to lines). <br> <br> | Checkbox ''transpose lists'': Columns are rotated by 90 degrees if checked (i.e. columns are transposed to lines). <br> <br> | ||
Checkbox ''copy ANN formatted weightings'': Activate this | Checkbox ''copy ANN formatted weightings'': Activate this check box to convert weightings into five different categories (bins) which can take values of 1 to 5. | ||
|} | |} | ||
Latest revision as of 15:19, 8 October 2025
Peak picking is an essential (and the final) step of the spectral pre-processing pipeline. The result of peak picking is a peak table which is attached to the mass spectra. In MicrobeMS peak picking can be started via the find peaks command of the Peak pick pulldown menu (shortcut <ctrl>+P), or by pressing the peak button located in the Peak pick tab.
Peak picking - basic concepts
Peak picking in MicrobeMS is always carried out on the basis of original, or pre-processed mass spectra, i.e. the content of existing peak table produced by software packages from other vendors will be ignored. The key idea of peak picking in MicrobeMS is based on two observations. Firstly, it is often convenient to limit the number of peaks per mass spectrum to pre-defined values. Secondly, the analytical sensitivity of MALDI-ToF mass spectrometry is different in different m/z regions: The sensitivity is higher in the low m/z region and lower in the high m/z region. These two observations are addressed with the procedure described next:
The first step of peak detection in MicrobeMS involves the generation of a so called threshold function represented by a S-shaped curve. Peaks can only be identified at m/z values with intensities above the threshold. In MicrobeMS the threshold function for peak picking is defined as the sum of the following m/z dependencies:
- i) A baseline function obtained by baseline correction by asymmetric least squares,
- ii) a S-shaped sigmoid function that reflects MALDI-ToF MS sensitivity as a function of m/z values, and
- iii) the noise distribution function multiplied by a constant.
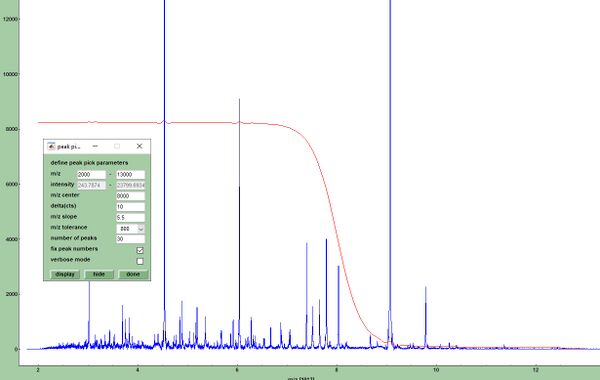
The sigmoid function (ii) is a special type of a generalized logistic function, which is defined by the following equation:
- (1),
where
- (2) and (3)
| the intensity threshold function, i.e. the S-shaped sigmoid function | |
| mean of the 13(-3) most intense mass peaks in the m/z range [mzlow mzhigh] of the given mass spectrum, 13(-3) means that the top 3 mass peaks are ignored | |
| variable scaling factor of | |
| slope, affects the slope of the threshold function around | |
| 'center' of the sigmoidal function, denotes the x-position at which asymptote maximum growth (pos, or neg) occurs | |
| the x-vector (in Th units) ranging from mzlow to mzhigh (2000 - 13000 Th per default) |
To obtain the peak tables the intensity threshold function T(m/z) is automatically obtained on the basis of parameters indicated in the window peak pick parameters. If the checkbox define number of peaks is not checked peak tables will contain only peaks with intensities larger than the threshold function. Otherwise the threshold function is scaled iteratively until the desired number of peaks is obtained.
When peak picking is complete a peak table array is created with npeaks rows and four or six columns (npeaks is the number of peaks in the table, see below for a description of the contents of the peak table). Peak tables are automatically added to the corresponding MS spectra and are displayed in a list box on the left side of the MicrobeMS main window, below the list box with the MicrobeMS spectra IDs. Note that existing peak tables may be overwritten without warning when new peak tables are created. Some computational details of the peak picking routine are available from the command line window if the peak pick verbose mode check box has been selected.
Peak picking - the procedure
To produce peak tables from raw mass spectra the following sequence of steps needs to be taken:
1. Load the mass spectral data files via the load spectra (Bruker data file format), import spectra from mzXML data, or the load MS multifile options of the File pull down menu.
2. Perform spectral pre-processing
3. Select the respective mass spectra in the list box at the top left corner (the list box is labeled by MicrobeMS spectra ID`s). To select multiple spectra hold the <shift> key while selecting.
4. Choose Peak pick parms (shortcut: <ctrl>+M) from the Peak pick pull down menu, or alternatively, press the button more in the Pick pick panel located at the central bottom of the main figure of MicrobeMS. A window entitled peak pick parameters comes up. Modify parameters of peak pick if necessary. When pressing the button display the intensity threshold function will be displayed. Hide removes this function from display. Press done to close this window, the values of modified parameters are not lost by this operation.
5. To start peak picking press the button peak (Peak pick panel) or select find peaks(shortcut: <ctrl>+P) from the Peak pick pull down menu. In cases where more than one spectrum has been selected a progress indicator will inform on the status of peak picking.
Format of peak tables
When peak picking has been finished, a peak table array containing npeaks rows and four columns is created (npeaks denotes the number of peaks in the table). The peak tables are attached to the spectral data files and contain the following columns:
- column #1: the m/z positions of the peaks
- column #2: the respective intensity values (intensity units). Note that the intensity values may represent intensities after baseline correction and normalization in cases where peak tables were obtained from pre-processed spectra.
- column #3: weighting factors (weights): these factors are obtained by scaling the values of column #2 (in a 1-norm manner) such that the sum of weighting factors contained in a given peak list equals 1000. Note that the ratios between the peak intensities are preserved.
- column #4: contains the intensity values of the threshold function (see above) at the m/z positions given by column #1
- column #5: FWHM (full width at half maximum) of the given peak (not always present, requires QT)
- column #6: resolving power of the peak (not always present, requires QT)
See also Description of the format of peak list files (*.pkf)
Function view peak tables
This function allows to view and copy peak list data. Press the view button in the Peak pick panel tab to view peak list data (see screenshot below).
| To copy the content of the columns peak positions [m/z], peak intensity [AU] (peak intensities from original, or pre-processed spectra), weightings [AU] (peak weighting factors), FWHM values (in m/z units), and, or resolving power, check the appropriate check boxes at the bottom of the dialog box and press copy. Checkbox transpose lists: Columns are rotated by 90 degrees if checked (i.e. columns are transposed to lines). |